|
Mitigation method
As this problem was caused by the conducted disturbance
wave from the IP-STB, four ferrite cores (Attenuation > 20 dB
@ 10-100 MHz) were installed on the component video cable as
shown in Figure 1.13-4. Figure 1.13-5 shows the variation of
the D/U ratio after the installation of those ferrite cores.
As the figure shows, the D/U ratio rose to about 45 dB, and
this problem was solved.
Figure 1.13-4 – Mitigation by ferrite cores
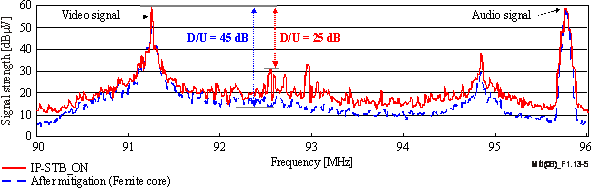
Figure 1.13-5 – Variation of D/U ratio after mitigation
Conclusion
In this NGN trial, communication and broadcasting
equipments are connected by cables such as a video cable;
therefore, both equipments can become disturbance sources. By
checking the spectrum of measured signals, in this case, it
was found that the IP-STB was a disturbance source. The
requirements of video ports should be defined to prevent EMC
problems on NGN services.
|



