Page 26 - Trends in Telecommunication Reform 2016
P. 26
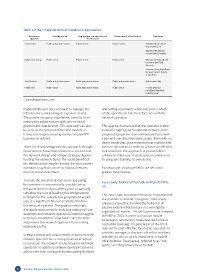
Table 1.2: Key characteristics of investment approaches
Investment Funding source Deployment and operations of Ownership of infrastructure Case study
approach infrastructure
Private DBO Public and private sectors Private sector Private sector •Mobile Infrastructure
Project (MIP), UK
•National Broadband
Scheme (NBS), Ireland
Public outsourcing Public sector Private sector Public sector •National ICT Broadband
Backbone (NICTBB),
Tanzania
•Johannesburg Broadband
Network Project (JBNP),
South Africa
Joint Venture Public and private sectors Public and private sectors Public and private sectors •Metroweb, Italy
Public DBO Public sector Public and private sectors Public sector • Qatar National
Broadband Network
(QNBN), Qatar
Source: Analysys Mason, 2015
responsibility and does not have to manage the and setting reasonable wholesale prices. Much
infrastructure, minimizing its exposure to risk. of the operational risk, therefore, lies with the
The private company, meanwhile, benefits from network operator.
owning the infrastructure with only minimal
government interference. This approach can also This approach assumes that the operator is able
be seen as the simplest of the PPP models, as to build a high-speed broadband network and is
it does not require creating overly complex PPP prepared to operate it on a wholesale basis, with
business structures. open and non-discriminatory access. Even with no
direct ownership, governments must monitor and
There are disadvantages to this approach, though. oversee operations in order to achieve an effective
Governments have little influence or control over outcome from this approach. A private DBO is
the network design and roll-out strategy, despite unlikely to make use of state assets in preference
funding the network build. The social benefit of to using and building its own assets.
the infrastructure may be limited, because private
operators may focus more on financial returns Two examples of private DBOs are set out in
than on social investment. greater detail below.
To make the investment case more appealing Case study: Mobile Infrastructure Project (MIP),
for operators in commercially unviable areas, UK
the government may provide a grant to partially
subsidize the cost of building the infrastructure. This case study was chosen because it approached
In return for the subsidy, the government would the problem of mobile "not-spots" from a very
expect a significant financial contribution from unique perspective: funding the build-out of
the network operator. The government might passive mobile infrastructure in a very tightly
also apply strict controls, including setting roll-out regulated UK market. The UK Government initiated
deadlines and network quality and take-up targets. the MIP in 2011 in order to improve mobile
In Europe, mandated "claw-back" rules for state coverage in remote and rural areas with little or
aid prevent the network operator from making no mobile coverage. In some areas of the UK, it
excessive profits.
may not be cost-effective for mobile operators to
provide coverage, as the low subscriber numbers
Setting controls and requirements ensures that the and density do not justify investment in mobile
network operator has a strong financial incentive infrastructure. These areas, referred to as "not-
to construct the network to the required technical spots," are the primary focus for MIP.
standards. In addition, network operators strive to
achieve the take-up targets by stimulating demand
8 Trends in Telecommunication Reform 2016