Page 78 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 78
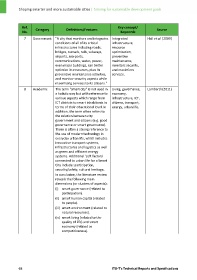
Ref. Category Definitions/Features Key concept/ Source
No. Keywords
7 Government "A city that monitors and integrates Integrated Hall et al. (2009)
conditions of all of its critical infrastructure,
infrastructures including roads, resource
bridges, tunnels, rails, subways, optimization,
airports, sea‐ports, preventive
communications, water, power, maintenance,
even major buildings, can better monitors security,
optimize its resources, plan its and maximizes
preventive maintenance activities, services.
and monitor security aspects while
maximizing services to its citizens."
8 Academic The term "smart city" is not used in Living, governance, Lombardi (2011)
a holistic way but with reference to economy,
various aspects which range from infrastructure, ICT,
ICT districts to smart inhabitants in citizens, transport,
terms of their educational level. In energy, urban life.
addition, the term often refers to
the relation between city
government and citizens (e.g. good
governance or smart governance).
There is often a strong reference to
the use of modern technology in
everyday urban life, which includes
innovative transport systems,
infrastructures and logistics as well
as green and efficient energy
systems. Additional 'soft factors'
connected to urban life for a Smart
City include: participation,
security/safety, cultural heritage.
In conclusion, the literature review
reveals the following main
dimensions (or clusters of aspects):
(i) smart governance (related to
participation).
(ii) smart human capital (related
to people).
(iii) smart environment (related to
natural resources).
(iv) smart living (related to the
quality of life) and smart
economy (related to
competitiveness).
68 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications